[04 Feb 2020] Longest Common Subsequence
Longest Common Subsequence
Examples:
LCS for input Sequences “ABCDGH” and “AEDFHR” is “ADH” of length 3.
LCS for input Sequences “AGGTAB” and “GXTXAYB” is “GTAB” of length 4.
Examples:
LCS for input Sequences “ABCDGH” and “AEDFHR” is “ADH” of length 3.
LCS for input Sequences “AGGTAB” and “GXTXAYB” is “GTAB” of length 4.
1) Optimal Substructure:
Let the input sequences be X[0..m-1] and Y[0..n-1] of lengths m and n respectively. And let L(X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1]) be the length of LCS of the two sequences X and Y. Following is the recursive definition of L(X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1]).
Let the input sequences be X[0..m-1] and Y[0..n-1] of lengths m and n respectively. And let L(X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1]) be the length of LCS of the two sequences X and Y. Following is the recursive definition of L(X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1]).
If last characters of both sequences match (or X[m-1] == Y[n-1]) then
L(X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1]) = 1 + L(X[0..m-2], Y[0..n-2])
L(X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1]) = 1 + L(X[0..m-2], Y[0..n-2])
If last characters of both sequences do not match (or X[m-1] != Y[n-1]) then
L(X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1]) = MAX ( L(X[0..m-2], Y[0..n-1]), L(X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-2]) )
L(X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1]) = MAX ( L(X[0..m-2], Y[0..n-1]), L(X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-2]) )
Examples:
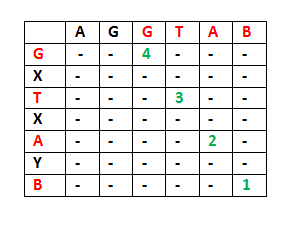
1) Consider the input strings “AGGTAB” and “GXTXAYB”. Last characters match for the strings. So length of LCS can be written as:
L(“AGGTAB”, “GXTXAYB”) = 1 + L(“AGGTA”, “GXTXAY”)
2) Consider the input strings “ABCDGH” and “AEDFHR. Last characters do not match for the strings. So length of LCS can be written as:
L(“ABCDGH”, “AEDFHR”) = MAX ( L(“ABCDG”, “AEDFHR”), L(“ABCDGH”, “AEDFH”) )
1) Consider the input strings “AGGTAB” and “GXTXAYB”. Last characters match for the strings. So length of LCS can be written as:
L(“AGGTAB”, “GXTXAYB”) = 1 + L(“AGGTA”, “GXTXAY”)

2) Consider the input strings “ABCDGH” and “AEDFHR. Last characters do not match for the strings. So length of LCS can be written as:
L(“ABCDGH”, “AEDFHR”) = MAX ( L(“ABCDG”, “AEDFHR”), L(“ABCDGH”, “AEDFH”) )
So the LCS problem has optimal substructure property as the main problem can be solved using solutions to subproblems.
2) Overlapping Subproblems:
Following is simple recursive implementation of the LCS problem. The implementation simply follows the recursive structure mentioned above.
Following is simple recursive implementation of the LCS problem. The implementation simply follows the recursive structure mentioned above.
/* A Naive recursive implementation of LCS problem */
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int max(int a, int b);
/* Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] */
int lcs( char *X, char *Y, int m, int n )
{
if (m == 0 || n == 0)
return 0;
if (X[m-1] == Y[n-1])
return 1 + lcs(X, Y, m-1, n-1);
else
return max(lcs(X, Y, m, n-1), lcs(X, Y, m-1, n));
}
/* Utility function to get max of 2 integers */
int max(int a, int b)
{
return (a > b)? a : b;
}
/* Driver code */
int main()
{
char X[] = "AGGTAB";
char Y[] = "GXTXAYB";
int m = strlen(X);
int n = strlen(Y);
cout<<"Length of LCS is "<< lcs( X, Y, m, n ) ;
return 0;
}
Output:
Length of LCS is 4
# A Naive recursive Python implementation of LCS problem
def lcs(X, Y, m, n):
if m == 0 or n == 0:
return 0;
elif X[m-1] == Y[n-1]:
return 1 + lcs(X, Y, m-1, n-1);
else:
return max(lcs(X, Y, m, n-1), lcs(X, Y, m-1, n));
# Driver program to test the above function
X = "AGGTAB"
Y = "GXTXAYB"
print "Length of LCS is ", lcs(X , Y, len(X), len(Y))
Output:
Length of LCS is 4
/* Dynamic Programming C++ implementation of LCS problem */
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int max(int a, int b);
/* Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] */
int lcs( char *X, char *Y, int m, int n )
{
int L[m + 1][n + 1];
int i, j;
/* Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] in
bottom up fashion. Note that L[i][j]
contains length of LCS of X[0..i-1]
and Y[0..j-1] */
for (i = 0; i <= m; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j <= n; j++)
{
if (i == 0 || j == 0)
L[i][j] = 0;
else if (X[i - 1] == Y[j - 1])
L[i][j] = L[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
else
L[i][j] = max(L[i - 1][j], L[i][j - 1]);
}
}
/* L[m][n] contains length of LCS
for X[0..n-1] and Y[0..m-1] */
return L[m][n];
}
/* Utility function to get max of 2 integers */
int max(int a, int b)
{
return (a > b)? a : b;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
char X[] = "AGGTAB";
char Y[] = "GXTXAYB";
int m = strlen(X);
int n = strlen(Y);
cout << "Length of LCS is "
<< lcs( X, Y, m, n );
return 0;
}
Output:
Length of LCS is 4
# Dynamic Programming implementation of LCS problem
def lcs(X , Y):
# find the length of the strings
m = len(X)
n = len(Y)
# declaring the array for storing the dp values
L = [[None]*(n+1) for i in xrange(m+1)]
"""Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] in bottom up fashion
Note: L[i][j] contains length of LCS of X[0..i-1]
and Y[0..j-1]"""
for i in range(m+1):
for j in range(n+1):
if i == 0 or j == 0 :
L[i][j] = 0
elif X[i-1] == Y[j-1]:
L[i][j] = L[i-1][j-1]+1
else:
L[i][j] = max(L[i-1][j] , L[i][j-1])
# L[m][n] contains the length of LCS of X[0..n-1] & Y[0..m-1]
return L[m][n]
#end of function lcs
# Driver program to test the above function
X = "AGGTAB"
Y = "GXTXAYB"
print "Length of LCS is ", lcs(X, Y)
Output:
Length of LCS is 4
Comments
Post a Comment